Understanding Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Systems.
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems are a modern HVAC solution that offers enhanced energy efficiency, flexibility, and comfort control. Unlike traditional HVAC systems, VRF systems can adjust refrigerant flow to multiple indoor units from a single outdoor unit, allowing for precise temperature control in different zones within a building.
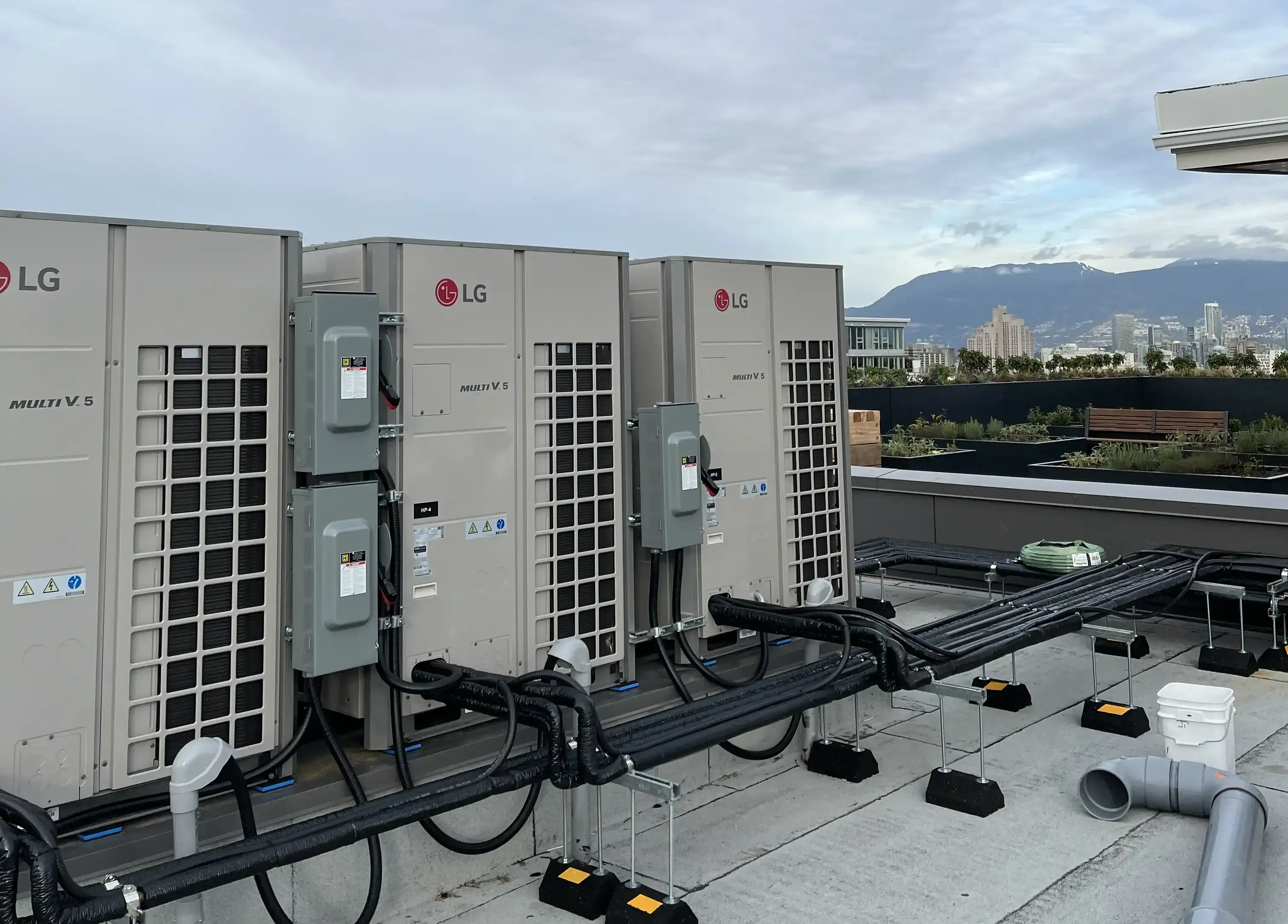

Trends in Commercial VRF Systems in North America.
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems are rapidly gaining popularity in North America’s commercial HVAC market due to their energy efficiency, flexibility, and ability to provide precise temperature control. As building owners seek sustainable solutions and lower operational costs, VRF systems have emerged as a leading technology trend.
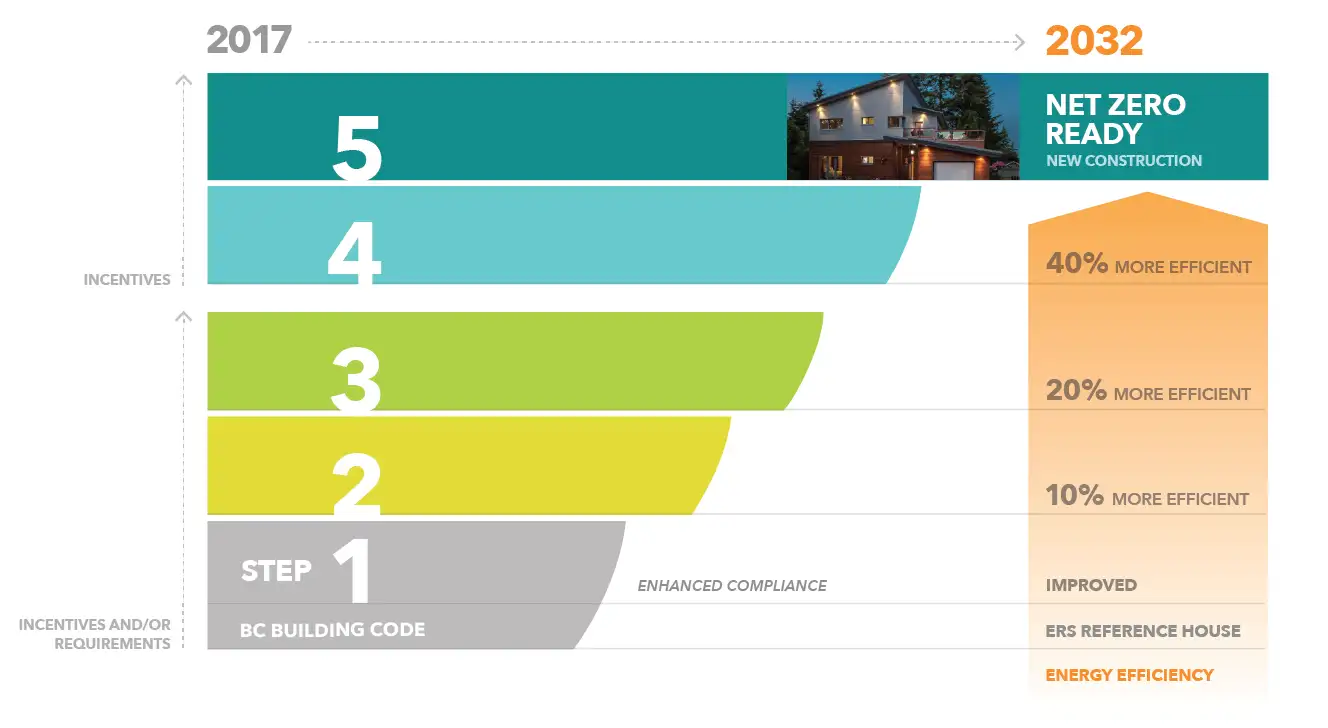
One major trend driving VRF adoption is the growing demand for energy-efficient solutions. With rising energy costs and stricter environmental regulations, businesses are turning to VRF systems to meet green building standards, including LEED certification and the BC Energy Step Code. These systems operate with fewer energy losses by adjusting refrigerant flow based on real-time demand, reducing consumption compared to traditional HVAC systems.
Additionally, integrating smart controls and building automation systems (BAS) has made VRF systems even more attractive. Businesses can now monitor energy usage, diagnose faults, and control multiple zones remotely, improving overall efficiency and comfort. As technology advances, the combination of VRF with IoT-enabled devices continues to simplify HVAC management.
Another key trend is the flexibility in design. VRF systems are particularly well-suited for retrofitting older buildings and supporting multi-zone spaces like hotels, office complexes, and mixed-use buildings. Their compact design and minimal ductwork allow installation in spaces where conventional systems are impractical.
Benefits of VRF Systems
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems offer several advantages over traditional HVAC systems, particularly regarding energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency and Savings.
- Dynamic Refrigerant Flow: VRF systems adjust the refrigerant flow based on demand, ensuring only the necessary energy is used to maintain desired temperatures. This results in significant energy savings compared to traditional systems.
- Inverter Technology: Inverter-driven compressors allow for fine adjustments in cooling and heating capacity, further reducing energy consumption.
- Design Flexibility and Ease of Installation: Compact and Modular Design: VRF systems require less ductwork and space, making them easier to install in various building layouts.
- Zoning Capabilities: They offer superior zoning capabilities, enabling personalized temperature settings for areas without extensive ductwork.
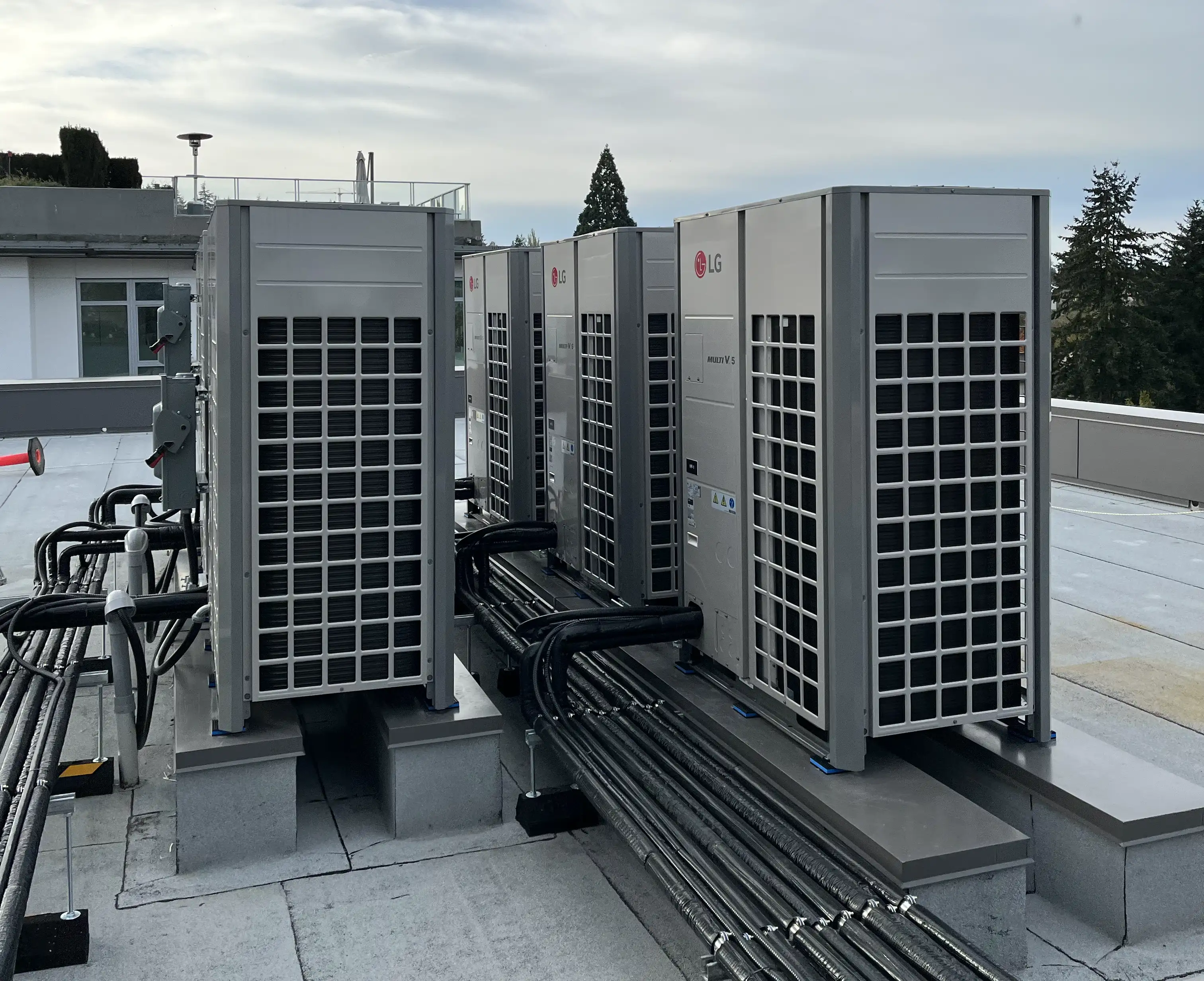

Reduced Maintenance Costs & Noise Reduction.
- Fewer Moving Parts: VRF systems are designed with reliability in mind, requiring less frequent maintenance and being less prone to breakdowns.
- Advanced Diagnostics: These systems often come with advanced diagnostics for easier maintenance and repair.
- Quiet Application: Using variable speed motors and inverter technology ensures that VRF systems operate quietly, enhancing occupant comfort.
Challenges and Complexities
VRF systems, while efficient, have historically presented challenges such as high initial costs, complex installation, and the need for specialized training. Their advanced controls and diagnostics require skilled technicians, adding to maintenance and operational complexities.
VRF system’s initial installation costs have become more competitive in the market when compared to other systems that provide full space heating and cooling, such as 4-pipe fan coil and hybrid heat pump systems. VRF solutions are being proposed more often in lieu of these systems for cost-saving purposes
Designing a VRF system requires careful planning to ensure optimal performance. This includes considerations for refrigerant piping lengths and zoning requirements.
Ensuring clean filters and clean coils to ensure efficiency is a requirement.
As per FHR2022 produced by the federal government large refrigeration systems require a leak test every year. For VRF systems this is obtained using the manufacturers required service tool, running data to verify the refrigerant charge. This data is saved to track the refrigerant charge over subsquent years. Other systems such as a large rooftop unit or chiller, mechanics can simply use a leak detector on the self-contained system, but for VRF this is not possible due to the hidden refrigerant pipes in the building.

Environmental Implications. Alignment with emerging policies.
In the US, the AIM Act (American Innovation and Manufacturing Act) aims to phase down the production and consumption of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), potent greenhouse gases used in refrigeration. VRF systems typically use HFC refrigerants like R-410A, which are being phased out under this act. Transitioning to alternative refrigerants aligns with the AIM Act’s goals.
The Green New Deal is a proposed package of policies addressing climate change and economic inequality. It emphasizes the transition to renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies. VRF systems contribute to these goals by reducing energy consumption and supporting sustainable building practices.
Conclusion
VRF systems represent a significant advancement in HVAC technology, offering numerous benefits such as energy efficiency, design flexibility, reduced maintenance costs, and noise reduction. The growing demand for sustainable construction is pushing VRF systems forward.
Governments and industry bodies are promoting eco-friendly technologies, driving VRF adoption as a solution that aligns with carbon reduction goals. While challenges such as higher upfront costs and the need for specialized labor persist, innovations in VRF technology are addressing these barriers.
As North America prioritizes energy efficiency and sustainability, VRF systems are poised to dominate the commercial HVAC market in the coming years.
Contact us today to learn more about VRF systems.